The demographic transition and the asset supply channel
Abstract
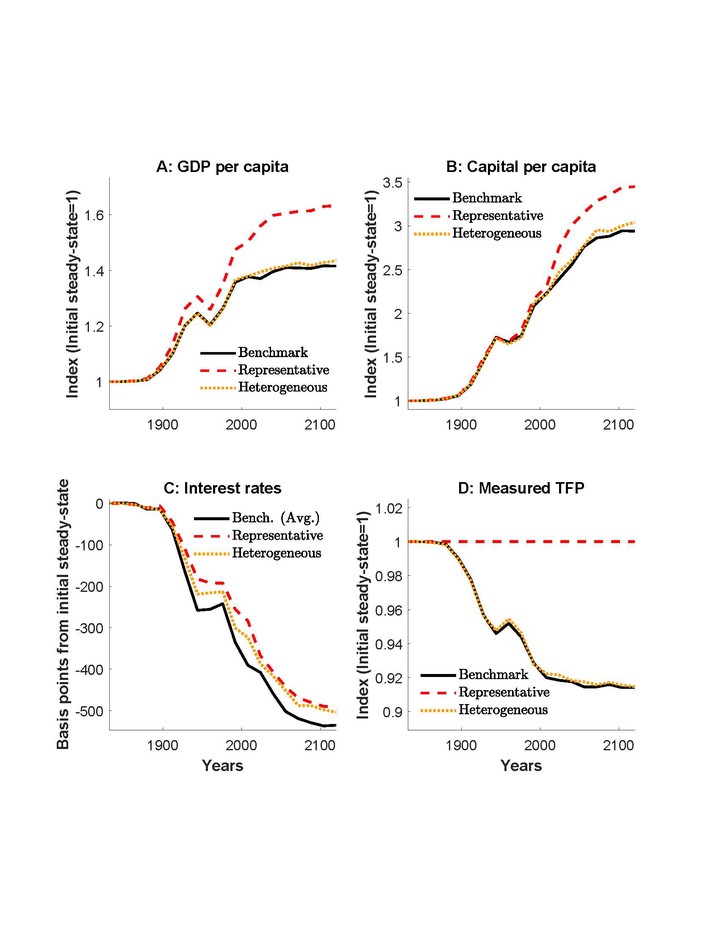
This paper examines the macroeconomic consequences of a demographic transition in an environment where a producer's capital structure is relevant, thereby introducing an asset supply channel. Producers are heterogeneous with respect to how productive they are in different states of the world, and may pursue different combinations of safe and/or risky securities issuance when financing projects. I simulate a demographic transition calibrated to replicate the US experience starting in 1880. This transition results in modest increases in output, larger increases in saving as a whole and, particularly, in a relative increase in saving in the form of safe assets. Lower capital costs lead to producer entry (and more issuance) and to a tilt towards safe issuance. I show that omitting this asset supply channel, as standard representative firm models do, results in a quantitatively important overestimation of the transmission effects of the demographic transition, with larger output gains despite smaller interest rate reductions.